用的是openmv3CamM7,最新版的固体版本
G
ggis 发布的帖子
-
为什么我用串口传输时,图像会变得像马赛克一样?发布在 OpenMV Cam
import sensor, image, time from pyb import UART import json # For color tracking to work really well you should ideally be in a very, very, # very, controlled enviroment where the lighting is constant... yellow_threshold = (65, 100, -10, 6, 24, 51) # You may need to tweak the above settings for tracking green things... # Select an area in the Framebuffer to copy the color settings. sensor.reset() # Initialize the camera sensor. sensor.set_pixformat(sensor.RGB565) # use RGB565. sensor.set_framesize(sensor.QQVGA) # use QQVGA for speed. sensor.skip_frames(10) # Let new settings take affect. sensor.set_auto_whitebal(False) # turn this off. clock = time.clock() # Tracks FPS. uart = UART(3, 115200) def find_max(blobs): max_size=0 for blob in blobs: if blob.pixels() > max_size: max_blob=blob max_size = blob.pixels() return max_blob while(True): img = sensor.snapshot() # Take a picture and return the image. blobs = img.find_blobs([yellow_threshold]) if blobs: max_blob=find_max(blobs) print('sum :', len(blobs)) img.draw_rectangle(max_blob.rect()) img.draw_cross(max_blob.cx(), max_blob.cy()) output_str="[%d,%d]" % (max_blob.cx(),max_blob.cy()) #方式1 #output_str=json.dumps([max_blob.cx(),max_blob.cy()]) #方式2 print('you send:',output_str) uart.write(output_str+'\r\n') else: print('not found!')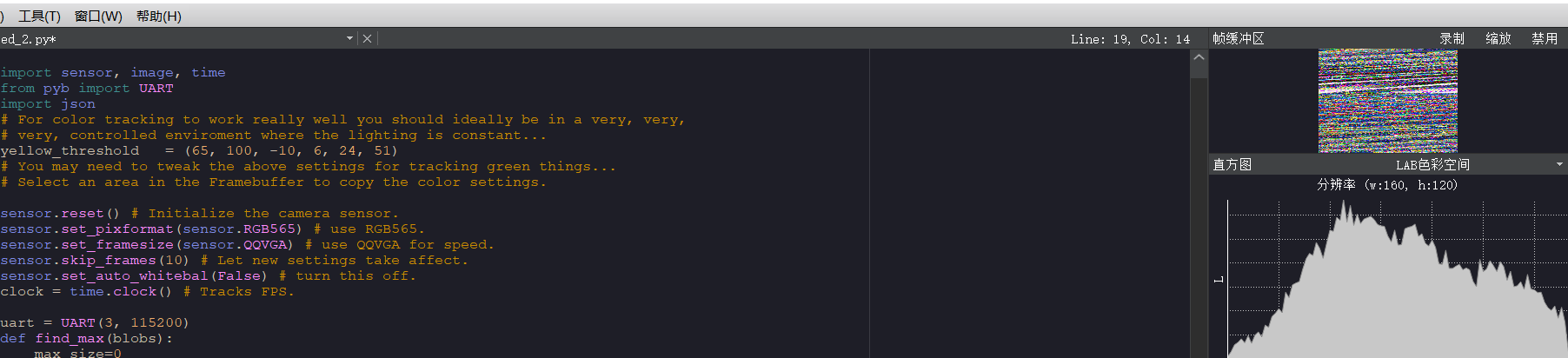
-
RE: I2C(-1, ...) is deprecated, use SoftI2C(...) instead ?发布在 OpenMV Cam
现在没有影响了,但是感觉运行速度好慢,三十几秒才一个循环
-
I2C(-1, ...) is deprecated, use SoftI2C(...) instead ?发布在 OpenMV Cam
import sensor, image, time, math import pyb from servo import Servos from machine import I2C, Pin sensor.reset() # 初始化摄像头 sensor.set_pixformat(sensor.RGB565) # 格式为 RGB565. sensor.set_framesize(sensor.QQVGA) # 使用 QQVGA 速度快一些 sensor.skip_frames(time = 2000) # 跳过2000s,使新设置生效,并自动调节白平衡 sensor.skip_frames(10) # Let new settings take affect. sensor.set_auto_gain(False) # 关闭自动自动增益。默认开启的,在颜色识别中,一定要关闭白平衡。 sensor.set_auto_whitebal(False) #关闭白平衡。白平衡是默认开启的,在颜色识别中,一定要关闭白平衡。 clock = time.clock() # 追踪帧率 i2c = I2C(sda=Pin('P5'), scl=Pin('P4')) servo = Servos(i2c, address=0x40, freq=50, min_us=650, max_us=2800, degrees=180) red_threshold = (87, 11, 127, 6, 2, 93) K=1400#the value should be measured得到mm x_chassis=0 y_chassis=0 x_camera=0 l_camera=0 i=0 arm_angle_goal=0 elbow_angle_goal=0 chassised_angle=0 chassised_angle_goal=0 chassis_angle_goal=0 arm_ball=0 chassis_ball=0 chassis_high=0 chassis_angle=0 #底盘舵机角度 arm_angle=0 #臂舵机角度 elbow_angle=0 #肘舵机角度 hand_angle=0 #手爪舵机角度 max_chassis_angle=180 #底盘舵机复位角度 min_chassis_angle=0 #底盘舵机有效角度 max_arm_angle=93 #臂舵机复位角度 min_arm_angle=0 #臂舵机有效角度 max_elbow_angle=180 #肘舵机复位角度 min_elbow_angle=0 #肘舵机有效角度 max_hand_angle=120 #手爪舵复位机角度 min_hand_angle=60 #手爪舵机有效角度 x_camera=0 #小球对于摄像头x坐标 y_camera=0 #小球对于摄像头y坐标 x_chassis=0 #小球对于底盘x坐标 y_chassis=0 #小球对于底盘y坐标 i=0 arm_angle_camera=0 #手臂和水平线角度 arm_ball=0 #臂舵机到球距离 elbow_angle_camera=0 #肘舵机于竖线的角度 chassis_high=50 #底座高度mm 90-20=70 arm_long=70 #手臂长度 elbow_hand_long=100 #手爪到肘长 chassis_ball=0 #底座到球距离 def find_max(blobs): max_size=0 for blob in blobs: if blob[2]*blob[3] > max_size: max_blob=blob max_size = blob[2]*blob[3] return max_blob while(True): time.sleep(3000) print('进入') while(i<11): i=i+1 clock.tick() # Track elapsed milliseconds between snapshots(). img = sensor.snapshot() # 从感光芯片获得一张图像 blobs = img.find_blobs([red_threshold]) if blobs: #如果找到了目标颜色 for b in blobs: #迭代找到的目标颜色区域 # Draw a rect around the blob. img.draw_rectangle(b[0:4]) # rect #用矩形标记出目标颜色区域 img.draw_cross(b[5], b[6]) # cx, cy #在目标颜色区域的中心画十字形标记 Lm = b[2]#+b[3])/2 length = K/Lm #球到摄像头距离 x_camera=x_camera+b[5] #为了求x点在感兴趣区域的坐标x平均 l_camera=l_camera+length #距离累加10次 print('正在获取小球对于球的坐标,距离,x坐标:',length,int(length),b[5]) #print(length) #print(b[5]) time.sleep(30) x_camera=x_camera/10 l_camera=l_camera/10 x_chassis=math.sin((x_camera-80)*115/160)*l_camera x_chassis=math.fabs(x_chassis) y_chassis=math.cos((x_camera-80)*115/160)*l_camera+80 #115是整个视野角度,平均到x方向每个像素就是115/160左边为负,右边为正,再乘以距离就是真实的偏移距离 print('得到数据,距离平均值mm,x坐标平均值,x绝对坐标,y绝对坐标,角度') time.sleep(30) print(l_camera) print(x_camera) print(x_chassis) print(y_chassis) print((x_camera-80)*115/160) #break #进入抓球状态 chassised_angle=math.atan(x_chassis/y_chassis) #得到相对弧度 chassised_angle=chassised_angle*180/3.14 #转换成角度 chassised_angle_goal=90-chassised_angle/0.34 #0.34=50/17 转换成舵机绝对角度 print('底盘绝对角度是:') print( chassised_angle) #arm_angle_goal和elbow_angle_goal是目标角度 chassis_ball=math.sqrt(x_chassis**2+y_chassis**2) arm_angle_goal=math.atan(chassis_high/chassis_ball) #角度:底座——球 & ——水平线 arm_ball=math.sqrt(chassis_ball*chassis_ball+chassis_high*chassis_high) #臂舵机到球距离 #手臂和水平线角度余弦定理c*c = a*a + b*b - 2*a*b*cosC求反余弦减去臂舵机到球距离 print( chassised_angle) arm_angle_goal=math.acos((arm_long**2 + arm_ball**2 - elbow_hand_long**2)/(2*arm_long*arm_ball))-arm_angle_goal arm_angle_goal= arm_angle_goal*180/math.pi #手臂和水平线角度 elbow_angle_goal = math.acos((elbow_hand_long*elbow_hand_long + arm_long*arm_long - arm_ball*arm_ball )/(2 * elbow_hand_long * arm_long))*180/math.pi#臂肘之间的角度 elbow_angle_goal = elbow_angle_goal-90+arm_angle_goal #肘舵机于竖线的角度 print('底座目标角度:') print(chassised_angle) print('手臂目标角度:') print(arm_angle_goal) print('肘部目标角度:') print(elbow_angle_goal) pass while(elbow_angle!=elbow_angle_goal or arm_angle!= arm_angle_goal or chassis_angle!= chassis_angle_goal or hand_angle!=min_hand_angle ): i=4 while(i>=0): i=i-1 if i==3 and hand_angle>min_hand_angle: servo.position(i,hand_angle) hand_angle-=1 elif i==2 and elbow_angle <= elbow_angle_goal: pass servo.position(i,elbow_angle) elbow_angle+=1 elif i==1 and arm_angle <= arm_angle_goal: pass servo.position(i,arm_angle) arm_angle+=1 elif i==0 and chassis_angle > chassis_angle_goal: ervo.position(i,chassis_angle) arm_angle-=1 elif i==0 and chassis_angle <= chassis_angle_goal: servo.position(i,chassis_angle) arm_angle+=1 while(min_hand_angle<=hand_angle): hand_angle+=1 servo.position(4,hand_angle) time.sleep(30) while(elbow_angle!=max_elbow_angle or arm_angle!=max_arm_angle or chassis_angle!=90): pass i=3 while(i>=0): #底座,手臂,肘,手爪,对应0,1,2,3 i=i-1 if i==2 and elbow_angle<=max_elbow_angle: servo.position(i,elbow_angle) elbow_angle+=1 elif i==1 and arm_angle<=max_arm_angle: servo.position(i,arm_angle) arm_angle+=1 elif i==0 and chassis_angle!=90: if chassis_angle<90: ervo.position(i,chassis_angle) arm_angle+=1 else: ervo.position(i,chassis_angle) arm_angle-=1 -
为什么我的openmv用起来很卡顿,延迟特别高???发布在 OpenMV Cam
# Blob Detection Example # # This example shows off how to use the find_blobs function to find color # blobs in the image. This example in particular looks for dark green objects. import sensor, image, time import car from pid import PID # You may need to tweak the above settings for tracking green things... # Select an area in the Framebuffer to copy the color settings. sensor.reset() # Initialize the camera sensor. sensor.set_pixformat(sensor.RGB565) # use RGB565. sensor.set_framesize(sensor.QQVGA) # use QQVGA for speed. sensor.skip_frames(10) # Let new settings take affect. sensor.set_auto_whitebal(False) # turn this off. clock = time.clock() # Tracks FPS. # For color tracking to work really well you should ideally be in a very, very, # very, controlled enviroment where the lighting is constant... green_threshold = (76, 96, -110, -30, 8, 66) size_threshold = 2000 x_pid = PID(p=0.5, i=1, imax=100) h_pid = PID(p=0.05, i=0.1, imax=50) def find_max(blobs): max_size=0 for blob in blobs: if blob[2]*blob[3] > max_size: max_blob=blob max_size = blob[2]*blob[3] return max_blob while(True): clock.tick() # Track elapsed milliseconds between snapshots(). img = sensor.snapshot() # Take a picture and return the image. blobs = img.find_blobs([green_threshold]) if blobs: max_blob = find_max(blobs) x_error = max_blob[5]-img.width()/2 h_error = max_blob[2]*max_blob[3]-size_threshold print("x error: ", x_error) ''' for b in blobs: # Draw a rect around the blob. img.draw_rectangle(b[0:4]) # rect img.draw_cross(b[5], b[6]) # cx, cy ''' img.draw_rectangle(max_blob[0:4]) # rect img.draw_cross(max_blob[5], max_blob[6]) # cx, cy x_output=x_pid.get_pid(x_error,1) h_output=h_pid.get_pid(h_error,1) print("h_output",h_output) car.run(-h_output-x_output,-h_output+x_output) else: car.run(18,-18)