@kidswong999 但是为什么识别一下卡那不会动半天出来线性回归不是一直动的
G
g23b 发布的帖子
-
巡线问题为什么会出现下面的问题?发布在 OpenMV Cam
为什么摄像头对这黑线后卡住一会才出来线性回归线而且不是实时的
BLACK_THRESHOLD = (34, 100, -61, 77, -76, 116)#(100, 55, -35, 22, 22, 82)#(3, 41, -3, 77, 12, 70)#(0, 95, 1, 34, 36, 80) #(5, 89, 35, 75, -8, 50)# Grayscale threshold for dark things... import sensor, image, time , math ,struct from pyb import UART from struct import pack, unpack import json sensor.reset() #sensor.set_vflip(True) #sensor.set_hmirror(True) sensor.set_pixformat(sensor.RGB565) sensor.set_framesize(sensor.QVGA) # 80x60 (4,800 pixels) - O(N^2) max = 2,3040,000. #sensor.set_auto_whitebal(False) # must be turned off for color tracking #sensor.set_windowing([0,20,80,40]) sensor.skip_frames(time = 2000) # WARNING: If you use QQVGA it may take seconds clock = time.clock() # to process a frame sometimes. uart = UART(3, 115200) while(True): clock.tick() img = sensor.snapshot().binary([BLACK_THRESHOLD]) line = img.get_regression([(100,100)], robust = True) if (line): rho_err = abs(line.rho())-img.width()/2 #计算一条直线与图像中央的距离 #坐标变换 xy轴的角度 if line.theta()>90: theta_err = line.theta()-180 else: theta_err = line.theta() img.draw_line(line.line(), color = 255)#127 output_str = "%f"%(theta_err) sumA = 0 sumB = 0 data = bytearray([0x41,0x43]) uart.write(data) data = bytearray([0x02,8]) for b in data: sumB = sumB + b sumA = sumA + sumB uart.write(data) float_value = theta_err float_bytes = pack('f', float_value) for b in float_bytes: sumB = sumB + b sumA = sumA + sumB uart.write(float_bytes) float_value = rho_err*0.1 float_bytes = pack('f', float_value) for b in float_bytes: sumB = sumB + b sumA = sumA + sumB uart.write(float_bytes) data = bytearray([sumB, sumA]) uart.write(data) print(float_value,theta_err) #print(rho_err*0.1) else: sumA = 0 sumB = 0 data = bytearray([0x41,0x43]) uart.write(data) data = bytearray([0x02,8]) for b in data: sumB = sumB + b sumA = sumA + sumB uart.write(data) float_value = 200 float_bytes = pack('f', float_value) for b in float_bytes: sumB = sumB + b sumA = sumA + sumB uart.write(float_bytes) float_value = 0 float_bytes = pack('f', float_value) for b in float_bytes: sumB = sumB + b sumA = sumA + sumB uart.write(float_bytes) data = bytearray([sumB, sumA]) uart.write(data) #print(theta_err) print(float_value) -
RE: 循环拍照并保存怎么保存不同的名字?发布在 OpenMV Cam
@kidswong999 语法解决啦,但是该如何第一次识别到拍照一次保存命名为1的照片识别第二次保存命名为2的照片 ,我的是识别后直接拍三张
-
循环拍照并保存怎么保存不同的名字?发布在 OpenMV Cam
循环拍照并保存怎么保存不同的名字?
import sensor, image, time, time, pyb from pyb import UART import json sensor.reset() sensor.set_pixformat(sensor.RGB565) sensor.set_framesize(sensor.QQVGA) sensor.skip_frames(time = 2000) sensor.set_auto_gain(False) # must be turned off for color tracking sensor.set_auto_whitebal(False) # must be turned off for color tracking clock = time.clock() uart = UART(3, 115200) while(True): clock.tick() img = sensor.snapshot().lens_corr(1.8) for r in img.find_rects(threshold=3500): #find_circles(threshold = 3500, x_margin = 10, y_margin = 10, r_margin = 10, r_min = 2, r_max = 100, r_step = 2).find_rects([roi=Auto, threshold=3500]) area = (r.rect()) #(c.x()-c.r(), c.y()-c.r(), 2*c.r(), 2*c.r()) #area为识别到的圆的区域,即圆的外接矩形框 statistics = img.get_statistics(roi=area) #像素颜色统计 print(statistics) #(0,100,0,120,0,120)是红色的阈值,所以当区域内的众数(也就是最多的颜色),范围在这个阈值内,就说明是红色的圆。 #l_mode(),a_mode(),b_mode()是L通道,A通道,B通道的众数。 if 0<statistics.l_mode()<100 and 0<statistics.a_mode()<120 and 0<statistics.b_mode()<120: #if the circle is red img.draw_rectangle(area,color=(255, 0, 0)) print("I am find ") #(c.x(), c.y(), c.r(), color = (255, 0, 0)) #识别到的红色区域用红色的圆框出来 r=200 uart.write(str(r)) #200回传到飞控 再m35模式里设置飞机悬停 也就是锁定xyz轴等待几秒运行下图拍照。 time.sleep_ms(10000) RED_LED_PIN = 1 BLUE_LED_PIN = 3 pyb.LED(RED_LED_PIN).on() time.sleep_ms(2000) # 给用户一个时间来准备 pyb.LED(RED_LED_PIN).off() time.sleep_ms(2000) pyb.LED(BLUE_LED_PIN).on() print("You're on camera!") img = sensor.snapshot() if n=1 n<4: n=n+0 print(n) img.morph(1, [+2, +1, +0,\ +1, +1, -1,\ +0, -1, -2]) # 浮雕图像 img.save("%d.jpg"%n) # or "example.bmp" (or others) pyb.LED(BLUE_LED_PIN).off() print("Done! Reset the camera to see the saved image.") else: print("Don't find") else: print("Don't find image.") -
怎样将下边的识别并拍照的代码循环3此以上?发布在 OpenMV Cam
import sensor, image, time, pyb, time sensor.reset() sensor.set_pixformat(sensor.RGB565) sensor.set_framesize(sensor.QQVGA) sensor.skip_frames(time = 2000) sensor.set_auto_gain(False) # must be turned off for color tracking sensor.set_auto_whitebal(False) # must be turned off for color tracking clock = time.clock() while(True): clock.tick() img = sensor.snapshot().lens_corr(1.8) for c in img.find_circles(threshold = 3500, x_margin = 10, y_margin = 10, r_margin = 10, r_min = 2, r_max = 100, r_step = 2): area = (c.x()-c.r(), c.y()-c.r(), 2*c.r(), 2*c.r()) #area为识别到的圆的区域,即圆的外接矩形框 statistics = img.get_statistics(roi=area) #像素颜色统计 print(statistics) #(0,100,0,120,0,120)是红色的阈值,所以当区域内的众数(也就是最多的颜色),范围在这个阈值内,就说明是红色的圆。 #l_mode(),a_mode(),b_mode()是L通道,A通道,B通道的众数。 if 0<statistics.l_mode()<100 and 0<statistics.a_mode()<127 and 0<statistics.b_mode()<127:#if the circle is red img.draw_circle(c.x(), c.y(), c.r(), color = (255, 0, 0)) #识别到的红色圆形用红色的圆框出来 else: img.draw_rectangle(area, color = (255, 255, 255)) #将非红色的圆用白色的矩形框出来 print("FPS %f" % clock.fps()) statistics=200 uart.write(str(kpts2)) #200回传到飞控 再n35模式里设置飞机悬停 也就是锁定xyz轴等待几秒运行下图拍照。 RED_LED_PIN = 1 BLUE_LED_PIN = 3 pyb.LED(RED_LED_PIN).on() sensor.skip_frames(time = 2000) # 给用户一个时间来准备 pyb.LED(RED_LED_PIN).off() pyb.LED(BLUE_LED_PIN).on() print("You're on camera!") img = sensor.snapshot() img.morph(1, [+2, +1, +0,\ +1, +1, -1,\ +0, -1, -2]) # 浮雕图像 img.save("1.jpg") # or "example.bmp" (or others) pyb.LED(BLUE_LED_PIN).off() print("Done! Reset the camera to see the saved image.") time.sleep_ms(1000) #延迟多久 -
为什么通信报错,我想知道怎么实现通信发布在 OpenMV Cam
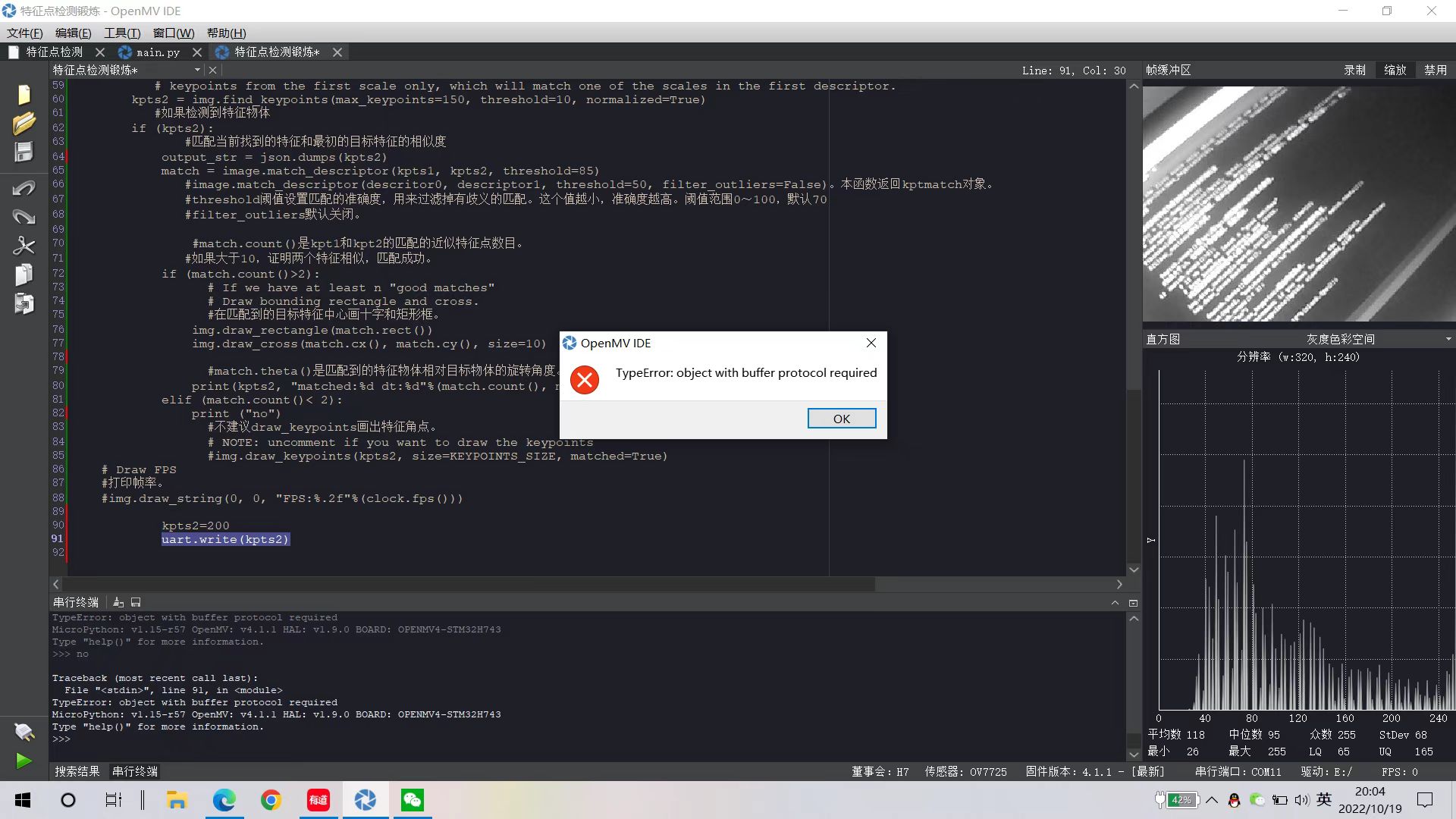
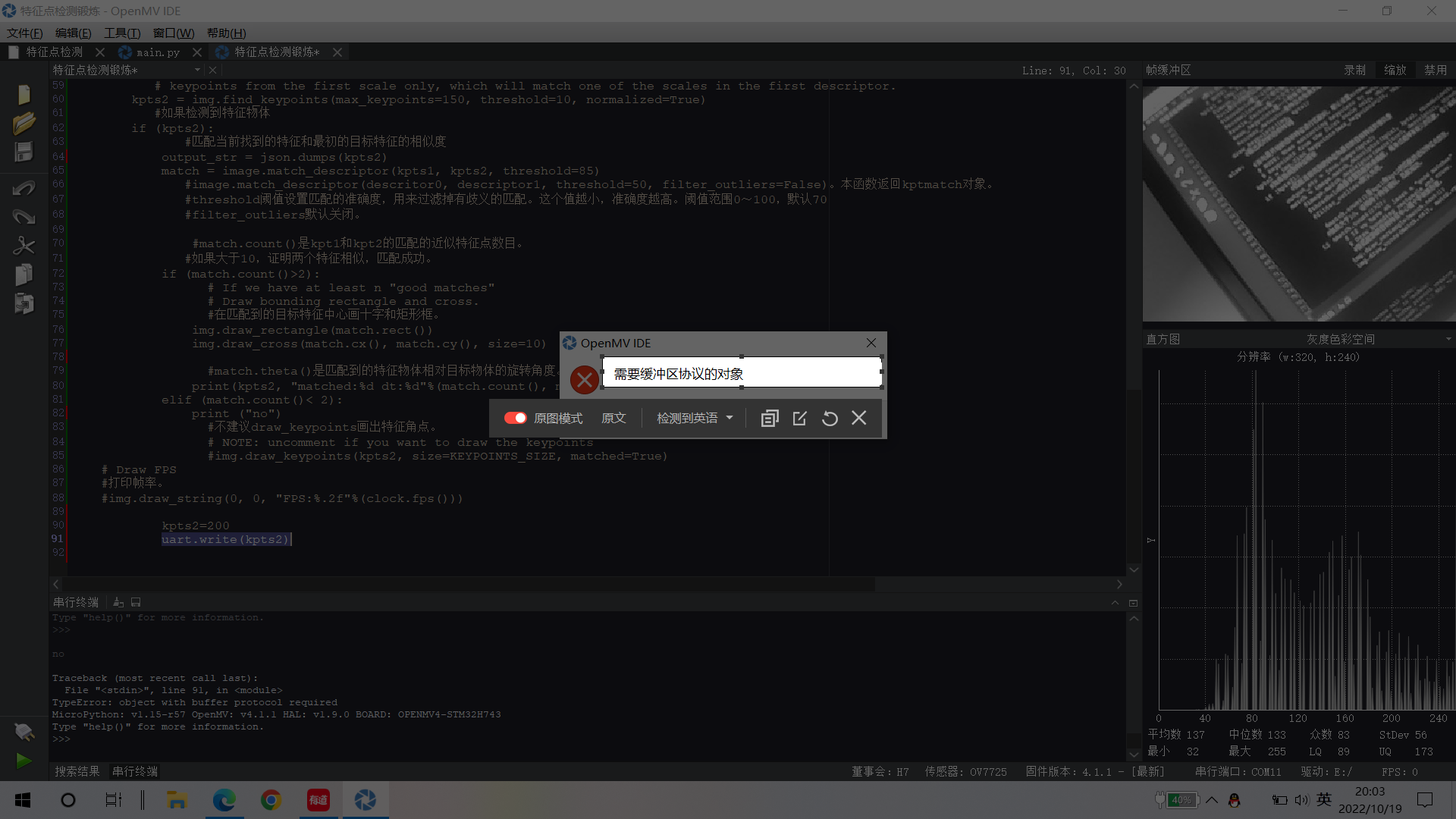
# 利用特征点检测特定物体例程。 # 向相机显示一个对象,然后运行该脚本。 一组关键点将被提取一次,然后 # 在以下帧中进行跟踪。 如果您想要一组新的关键点,请重新运行该脚本。 # 注意:请参阅文档以调整find_keypoints和match_keypoints。 import sensor, time, image, math, struct from pyb import UART from struct import pack, unpack import json sensor.reset() # Sensor settings sensor.set_contrast(3) sensor.set_gainceiling(16) sensor.set_framesize(sensor.VGA) sensor.set_windowing((320, 240)) sensor.set_pixformat(sensor.GRAYSCALE) sensor.skip_frames(time = 2000) sensor.set_auto_gain(False, value=100) clock = time.clock() # to process a frame sometimes. uart = UART(1, 115200) #画出特征点 def draw_keypoints(img, kpts): if kpts: print(kpts) img.draw_keypoints(kpts) img = sensor.snapshot() time.sleep_ms(1000) #kpts1 = None #kpts1保存目标物体的特征,可以从文件导入特征,但是不建议这么做。 kpts1 = image.load_descriptor("/desc.orb") img = sensor.snapshot() #draw_keypoints(img, kpts1) clock = time.clock() while (True): clock.tick() img = sensor.snapshot() if (kpts1 == None): #如果是刚开始运行程序,提取最开始的图像作为目标物体特征,kpts1保存目标物体的特征 #默认会匹配目标特征的多种比例大小,而不仅仅是保存目标特征时的大小,比模版匹配灵活。 # NOTE: By default find_keypoints returns multi-scale keypoints extracted from an image pyramid. kpts1 = img.find_keypoints(max_keypoints=150, threshold=10, scale_factor=1.2) #image.find_keypoints(roi=Auto, threshold=20, normalized=False, scale_factor=1.5, max_keypoints=100, corner_detector=CORNER_AGAST) #roi表示识别的区域,是一个元组(x,y,w,h),默认与framsesize大小一致。 #threshold是0~255的一个阈值,用来控制特征点检测的角点数量。用默认的AGAST特征点检测,这个阈值大概是20。用FAST特征点检测,这个阈值大概是60~80。阈值越低,获得的角点越多。 #normalized是一个布尔数值,默认是False,可以匹配目标特征的多种大小(比ncc模版匹配效果灵活)。如果设置为True,关闭特征点检测的多比例结果,仅匹配目标特征的一种大小(类似于模版匹配),但是运算速度会更快一些。 #scale_factor是一个大于1.0的浮点数。这个数值越高,检测速度越快,但是匹配准确率会下降。一般在1.35~1.5左右最佳。 #max_keypoints是一个物体可提取的特征点的最大数量。如果一个物体的特征点太多导致RAM内存爆掉,减小这个数值。 #corner_detector是特征点检测采取的算法,默认是AGAST算法。FAST算法会更快但是准确率会下降。 draw_keypoints(img, kpts1) #画出此时的目标特征 else: #当与最开始的目标特征进行匹配时,默认设置normalized=True,只匹配目标特征的一种大小。 # NOTE: When extracting keypoints to match the first descriptor, we use normalized=True to extract # keypoints from the first scale only, which will match one of the scales in the first descriptor. kpts2 = img.find_keypoints(max_keypoints=150, threshold=10, normalized=True) #如果检测到特征物体 if (kpts2): #匹配当前找到的特征和最初的目标特征的相似度 output_str = json.dumps(kpts2) match = image.match_descriptor(kpts1, kpts2, threshold=85) #image.match_descriptor(descritor0, descriptor1, threshold=50, filter_outliers=False)。本函数返回kptmatch对象。 #threshold阈值设置匹配的准确度,用来过滤掉有歧义的匹配。这个值越小,准确度越高。阈值范围0~100,默认70 #filter_outliers默认关闭。 #match.count()是kpt1和kpt2的匹配的近似特征点数目。 #如果大于10,证明两个特征相似,匹配成功。 if (match.count()>2): # If we have at least n "good matches" # Draw bounding rectangle and cross. #在匹配到的目标特征中心画十字和矩形框。 img.draw_rectangle(match.rect()) img.draw_cross(match.cx(), match.cy(), size=10) #match.theta()是匹配到的特征物体相对目标物体的旋转角度。 print(kpts2, "matched:%d dt:%d"%(match.count(), match.theta())) elif (match.count()< 2): print ("no") #不建议draw_keypoints画出特征角点。 # NOTE: uncomment if you want to draw the keypoints #img.draw_keypoints(kpts2, size=KEYPOINTS_SIZE, matched=True) # Draw FPS #打印帧率。 #img.draw_string(0, 0, "FPS:%.2f"%(clock.fps())) kpts2=200 uart.write(kpts2)